- ANOVA - Null Hypothesis
- Test Statistic - F
- Assumptions for ANOVA
- Effect Size - (Partial) Eta Squared
- ANOVA - Post Hoc Tests
ANOVA -short for “analysis of variance”- is a statistical technique
for testing if 3(+) population means are all equal.
The two simplest scenarios are
- one-way ANOVA for comparing 3(+) groups on 1 variable: do all children from school A, B and C have equal mean IQ scores? For 2 groups, one-way ANOVA is identical to an independent samples t-test.
- repeated measures ANOVA for comparing 3(+) variables in 1 group: is the mean rating for beer A, B and C equal for all people?For 2 variables, repeated measures ANOVA is identical to a paired samples t-test.
The figure below visualizes the basic question for one-way ANOVA.
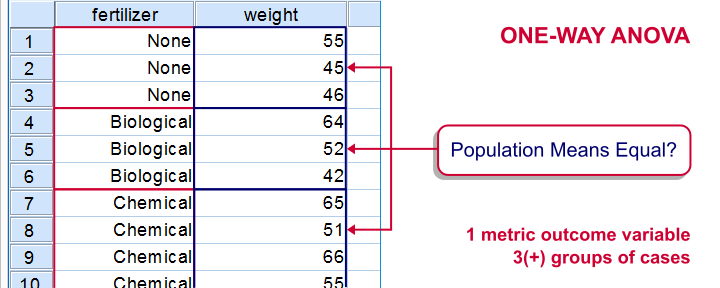
Simple Example - One-Way ANOVA
A scientist wants to know if all children from schools A, B and C have equal mean IQ scores. Each school has 1,000 children. It takes too much time and money to test all 3,000 children. So a simple random sample of n = 10 children from each school is tested.
Part of these data -available from this Googlesheet are shown below.
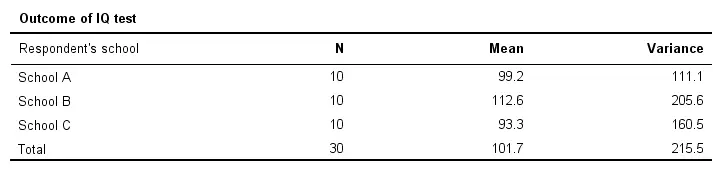
Descriptives Table
Right, so our data contain 3 samples of 10 children each with their IQ scores. Running a simple descriptives table immediately tells us the mean IQ scores for these samples. The result is shown below.
For making things clearer, let's visualize the mean IQ scores per school in a simple bar chart.
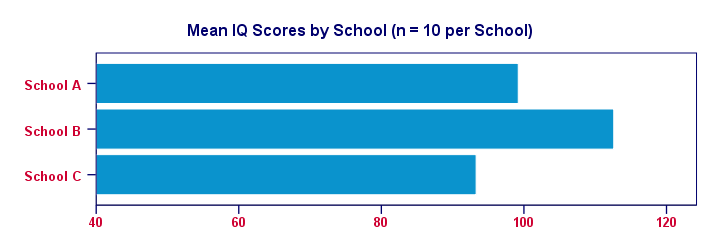
Clearly, our sample from school B has the highest mean IQ - roughly 113 points. The lowest mean IQ -some 93 points- is seen for school C.
Now, here's the problem: our mean IQ scores are only based on tiny samples of 10 children per school. So couldn't it be that
all 1,000 children per school have the same mean IQ?
Perhaps we just happened to sample the smartest children from school B and the dumbest children from school C?“Dumbest” isn't really appropriate here: these children may have terrific talents that -unfortunately for them- aren't measured by the test adminstered. However, a discussion of the usefulness of IQ tests is beyond the scope of this tutorial. Is that realistic? We'll try and show that this statement -our null hypothesis- is not credible given our data.
ANOVA - Null Hypothesis
The null hypothesis for (any) ANOVA is that all population means are exactly equal. If this holds, then our sample means will probably differ a bit. After all, samples always differ a bit from the populations they represent. However, the sample means probably shouldn't differ too much. Such an outcome would be unlikely under our null hypothesis of equal population means. So if we do find this, we'll probably no longer believe that our population means were really equal.
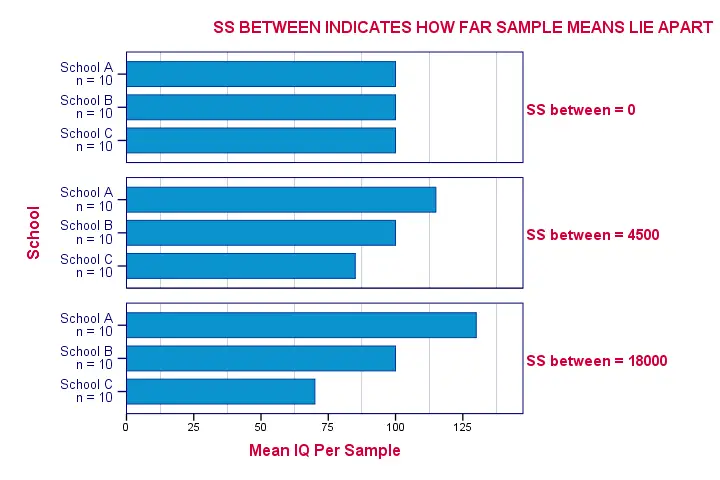
ANOVA - Sums of Squares Between
So precisely how different are our 3 sample means? How far do these numbers lie apart? A number that tells us just that is the variance. So we'll basically compute the variance among our 3 sample means.
As you may (or may not) understand from the ANOVA formulas, this starts with the sum of the squared deviations between the 3 sample means and the overall mean. The outcome is known as the “sums of squares between” or SSbetween. So
sums of squares between expresses
the total amount of dispersion among the sample means.
Everything else equal, larger SSbetween indicates that the sample means differ more. And the more different our sample means, the more likely that our population means differ as well.
Degrees of Freedom and Mean Squares Between
When calculating a “normal” variance, we divide our sums of squares by its degrees of freedom (df). When comparing k means, the degrees of freedom (df) is (k - 1).
Dividing SSbetween by (k - 1) results in mean squares between: MSbetween. In short,
mean squares between
is basically the variance among sample means.
MSbetween thus indicates how far our sample means differ (or lie apart). The larger this variance between means, the more likely that our population means differ as well.
ANOVA - Sums of Squares Within
If our population means are really equal, then what difference between sample means -MSbetween- can we reasonably expect? Well, this depends on the variance within subpopulations. The figure below illustrates this for 3 scenarios.
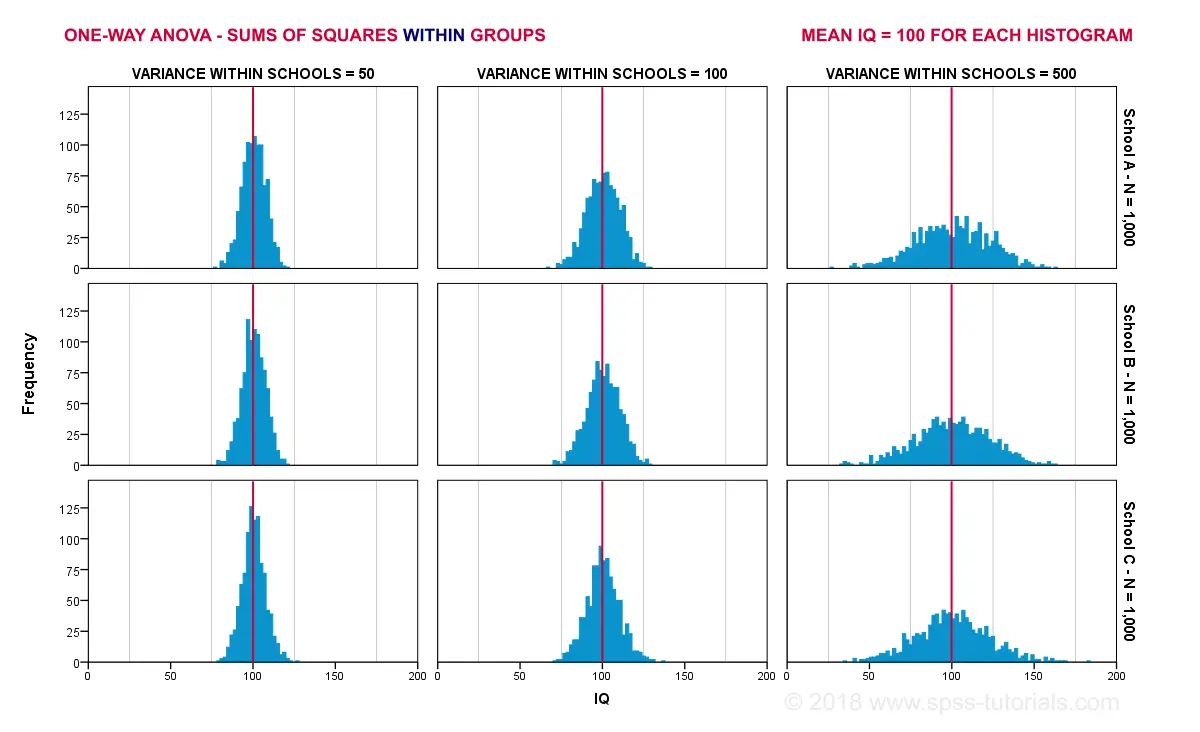
The 3 leftmost histograms show population distributions for IQ in schools A, B and C. Their narrowness indicates a small variance within each school. If we'd sample n = 10 students from each school,
should we expect very different sample means?
Probably not. Why? Well, due to the small variance within each school, the sample means will be close to the (equal) population means. These narrow histograms don't leave a lot of room for their sample means to fluctuate and -hence- differ.
The 3 rightmost histograms show the opposite scenario: the histograms are wide, indicating a large variance within each school. If we'd sample n = 10 students from each school, the means in these samples may easily differ quite a lot. In short,
larger variances within schools probably result in a
larger variance between sample means per school.
We basically estimate the within-groups population variances from the within-groups sample variances. Makes sense, right? The exact calculations are in the ANOVA formulas and this Googlesheet. In short:
- sums of squares within (SSwithin) indicates the total amount of dispersion within groups;
- degrees of freedom within (DFwithin) is (n - k) for n observations and k groups and
- mean squares within (MSwithin) -basically the variance within groups- is SSwithin / DFwithin.
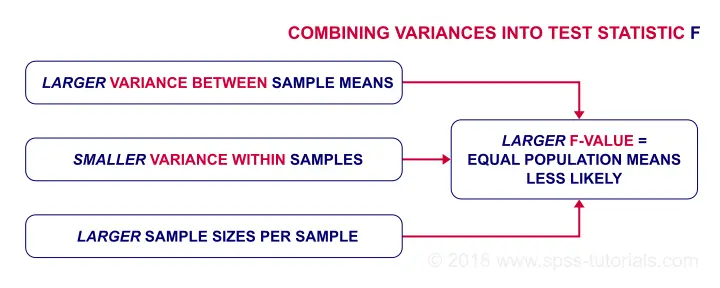
ANOVA Test Statistic - F
So how likely are the population means to be equal? This depends on 3 pieces of information from our samples:
- the variance between sample means (MSbetween);
- the variance within our samples (MSwithin) and
- the sample sizes.
We basically combine all this information into a single number: our test statistic F. The diagram below shows how each piece of evidence impacts F.
Now, F itself is not interesting at all. However, we can obtain the statistical significance from F if it follows an F-distribution. It will do just that if 3 assumptions are met.
ANOVA - Assumptions
The assumptions for ANOVA are
- independent observations;
- normality: the outcome variable must follow a normal distribution in each subpopulation. Normality is really only needed for small sample sizes, say n < 20 per group.
- homogeneity: the variances within all subpopulations must be equal. Homogeneity is only needed if sample sizes are very unequal. In this case, Levene's test indicates if it's met.
If these assumptions hold, then F follows an F-distribution with DFbetween and DFwithin degrees of freedom. In our example -3 groups of n = 10 each- that'll be F(2,27).
ANOVA - Statistical Significance
In our example, F(2,27) = 6.15. This huge F-value is strong evidence that our null hypothesis -all schools having equal mean IQ scores- is not true. If all assumptions are met, F follows the F-distribution shown below.
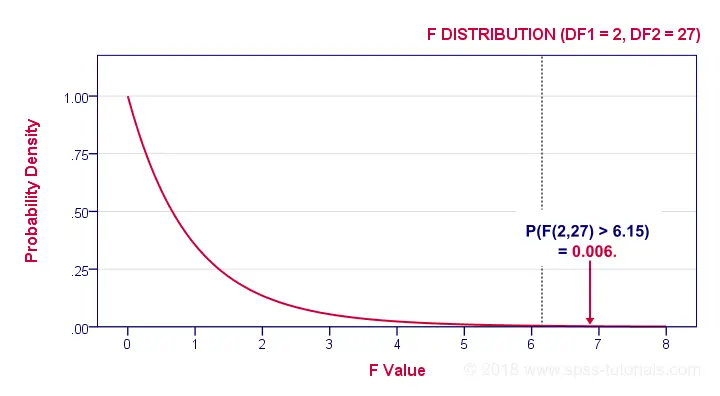
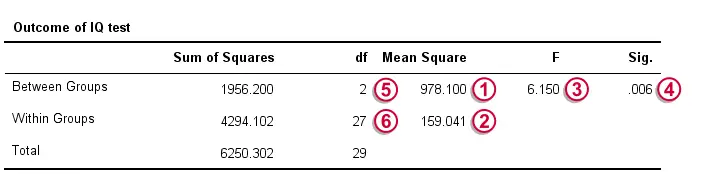
Given this distribution, we can look up that the statistical significance. We usually report: F(2,27) = 6.15, p = 0.006. If our schools have equal mean IQ's, there's only a 0.006 chance of finding our sample mean differences or larger ones. We usually say something is “statistically significant” if p < 0.05. Conclusion: our population means are very unlikely to be equal. The figure below shows how SPSS presents the output for this example.
Effect Size - (Partial) Eta Squared
So far, our conclusion is that the population means are not all exactly equal. Now, “not equal” doesn't say much. What I'd like to know is
exactly how different are the means?
A number that estimates just that is the effect size. An effect size measure for ANOVA is partial eta squared, written as η2.η is the Greek letter “eta”, pronounced as a somewhat prolonged “e”. For a one-way ANOVA, partial eta-squared is equal to simply eta-squared.
Technically,
(partial) eta-squared is the
proportion of variance accounted for by a factor.
Some rules of thumb are that
- η2 > 0.01 indicates a small effect;
- η2 > 0.06 indicates a medium effect;
- η2 > 0.14 indicates a large effect.
The exact calculation of eta-squared is shown in the formulas section. For now, suffice to say that η2 = 0.31 for our example. This huge -huge- effect size explains why our F-test is statistically significant despite our very tiny sample sizes of n = 10 per school.
Post Hoc Tests - Tukey's HSD
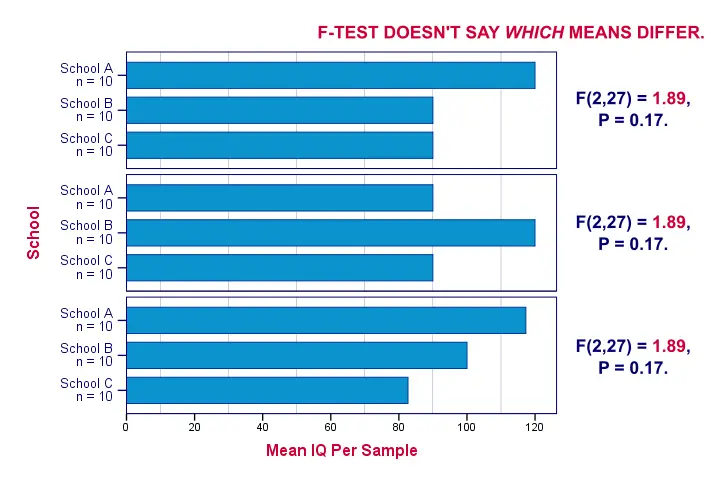
So far, we concluded from our F-test that our population means are very unlikely to be (all) equal. The effect size, η2, told us that the difference is large. An unanswered question, though, is precisely which means are different? Different patterns of sample means may all result in the exact same F-value. The figure below illustrates this point with some possible scenarios.
One approach would be running independent samples t-tests on all possible pairs of means. For 3 means, that'll be A-B, A-C and B-C. However, as the number of means we compare grows, the number of all possible pairs rapidly increases.Precisely, k means result in 0.5 * k * (k - 1) distinct pairs. Like so, 3 means have 3 distinct pairs, 4 means have 6 distinct pairs and 5 means have 10 distinct pairs. And
each t-test has its own chance of drawing a wrong conclusion.
So the more t-tests we run, the bigger the risk of drawing at least one wrong conclusion.
The most common solution to this problem is using Tukey's HSD (short for “Honestly Significant Difference”) procedure. You could think of it as running all possible t-tests for which the results have been corrected with some sort of Bonferroni correction but less conservative. The figure below shows some output from Tukey's HSD in SPSS.
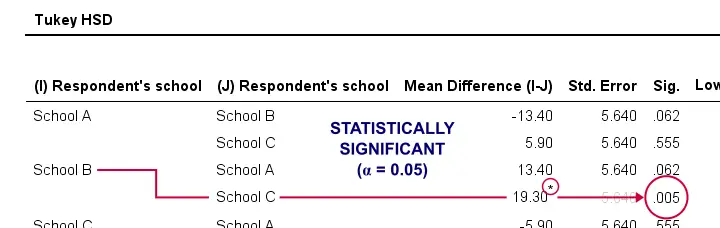
Tukey's HSD is known as a post hoc test. “Post hoc” is Latin and literally means “after that”. This is because they are run only after the main F-test has indicated that not all means are equal. I don't entirely agree with this convention because
- post hoc tests may not indicate differences while the main F-test does;
- post hoc tests may indicate differences while the main F-test does not.
Say I'm comparing 5 means: A, B, C and D are equal but E is much larger than the others. In this case, the large difference between E and the other means will be strongly diluted when testing if all means are equal. So in this case
an overall F-test may not indicate any differences
while post hoc tests will.
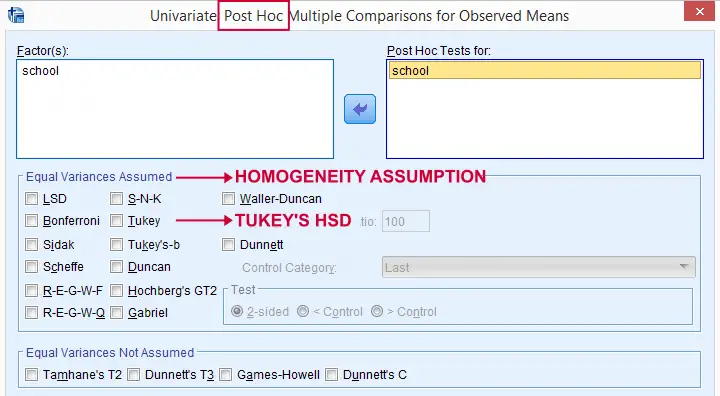
Last but not least, there's many other post hoc tests as well. Some require the homogeneity assumption and others don't. The figure below shows some examples.
ANOVA - Basic Formulas
For the sake of completeness, we'll list the main formulas used for the one-way ANOVA in our example. You can see them in action in this Googlesheet.
We'll start off with the between-groups variance:
$$SS_{between} = \Sigma\;n_j\;(\overline{X}_j - \overline{X})^2$$
where
- \(\overline{X}_j\) denotes a group mean;
- \(\overline{X}\) is the overall mean;
- \(n_j\) is the sample size per group.
For our example, this results in
$$SS_{between} = 10\;(99.2 - 101.7)^2 + 10\;(112.6 - 101.7)^2 + 10\;(93.3 - 101.7)^2 = 1956.2 $$
Next, for \(m\) groups,
$$df_{between} = m - 1$$
so \(df_{between}\) = 3 - 1 = 2 for our example data.
$$MS_{between} = \frac{SS_{between}}{df_{between}}$$
For our example, that'll be
$$\frac{1956.2}{2} = 978.1$$
We now turn to the within-groups variance. First off,
$$SS_{within} = \Sigma\;(X_i - \overline{X}_j)^2$$
where
- \(\overline{X}_j\) denotes a group mean;
- \(X_i\) denotes an individual observation (“data point”).
For our example, this'll be
$$SS_{within} = (90 - 99.2)^2 + (87 - 99.2)^2 + ... + (96 - 93.3)^2 = 4294.1$$
for \(n\) independent observations and \(m\) groups,
$$df_{within} = n - m$$
So for our example that'll be = 30 - 3 = 27.
$$MS_{within} = \frac{SS_{within}}{df_{within}}$$
For our example, this results in
$$\frac{4294.1}{27} = 159$$
We're now ready to calculate the F-statistic:
$$F = \frac{MS_{between}}{MS_{within}}$$
which results in
$$\frac{978.1}{159} = 6.15$$
Finally,
$$P = P(F(2,27) > 6.15) = 0.0063$$
Optionally, the effect size η2 is calculated as
$$Effect\;\;size\;\;\eta^2 = \frac{SS_{between}}{SS_{between} + SS_{within}}$$
For our example, that'll be
$$\frac{1956.2}{1956.2 + 4294.1} = 0.31$$
Thanks for reading.
 SPSS TUTORIALS
SPSS TUTORIALS
THIS TUTORIAL HAS 61 COMMENTS:
By Babak on January 13th, 2023
honestly, I think this article is very educative. l learnt a great deal about ANOVA and its respective effect size both conceptually and technically. Thank you so much!